Effective online and blended learning goes beyond using technology as a mere hub for learning materials. It is about creating dynamic, engaging, and flexible learning environments that align with Universal Design for Learning (UDL) principles. As an educator using Canvas, I have come to realize that true engagement in online spaces requires thoughtful design that leverages interactive tools, encourages collaboration, and accommodates diverse learning styles.
What Does Online and Blended Learning Look Like in Mathematics Education?
Online and blended learning are often misunderstood as digital versions of traditional face-to-face instruction. However, their potential lies in their ability to reshape the learning experience. In my experience as a mathematics educator, maximizing engagement in Canvas involves incorporating interactive simulations and digital manipulatives that allow students to visualize abstract concepts such as functions and geometric transformations. Incorporating these within Canvas modules has helped students engage in explorations of functions, fostering deeper understanding through immediate feedback and real-world application.
Blended learning, in particular, offers a powerful synergy between in-person interactions and digital flexibility. My classes utilize a learning model where students have access to instructional videos and guided practice within Canvas. Students have access to instructional videos outside of the classroom, and Canvas acts as a platform for assignment submission, interactive practice, and projects. This approach has not only enhanced student autonomy but also allowed for more individualized support during face-to-face sessions.
According to Conceição and Howles (2020), designing an effective online learning environment requires careful consideration of both the course structure and the learner interface. A well-structured course aligns content organization with clear learning objectives, ensuring that students can navigate the material intuitively and meaningfully. For instance, in my mathematics courses, I structure modules around key competencies and organize the course with clear progression paths and milestone checks to maintain student motivation.
Leveraging Learning Management Systems for Effective Mathematics Instruction
A critical component in achieving these goals is the effective use of Learning Management Systems (LMS). As Rottmann, Barreto, and Rabidoux (2020) suggest, institutions and organizations adopt LMS platforms for several reasons, such as centralizing content, providing 24/7 access, offering flexibility for on-demand learning, and streamlining processes like communication and tracking student progress. In my practice, utilizing the analytics tools in Canvas has provided insights into student engagement patterns, helping me identify those who may need additional support.
However, as Conceição and Howles (2020) highlight, the LMS is only as effective as the strategies employed within it. Simply uploading materials is not enough. Educators must take advantage of the system’s capabilities to create engaging, interactive learning experiences that align with pedagogical goals. I have found that incorporating interactive textbooks increases engagement, encouraging peer-to-peer learning and diverse problem-solving strategies.
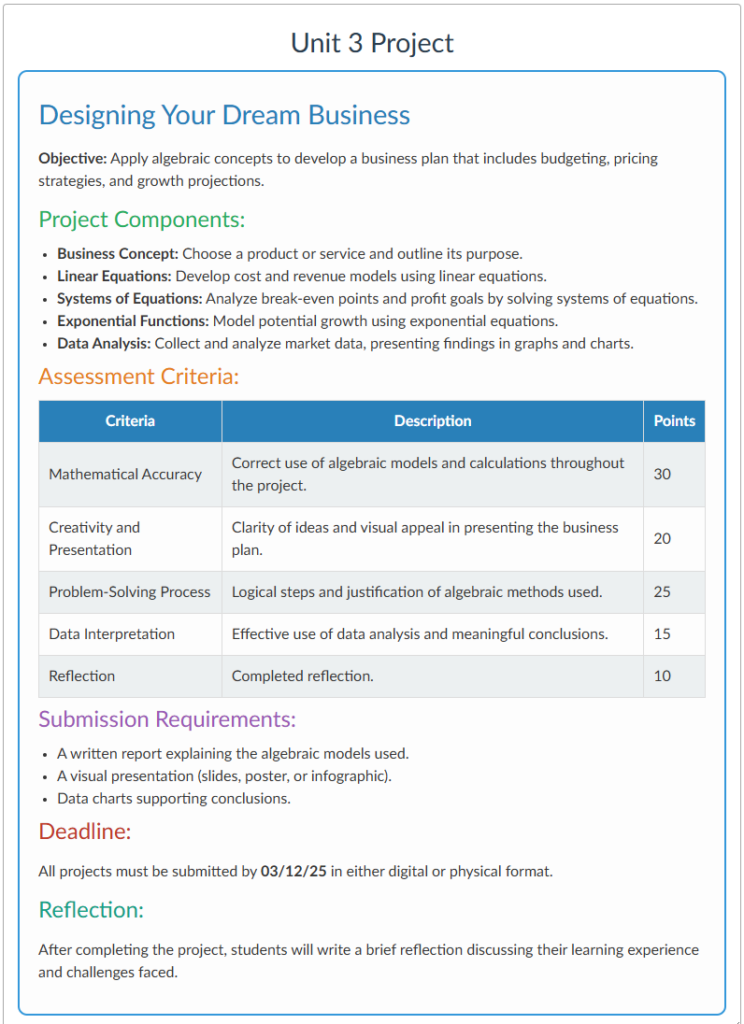
Improving Learning Outcomes Through Thoughtful Design
To truly harness the potential of online and blended learning, educators must adopt a design-thinking approach that prioritizes the learner experience. This means considering the structure, navigation, and visual design of the course to make learning intuitive and accessible. Ensuring that modules include content in multiple formats can support students with diverse learning profiles.
Incorporating interactive elements such as quizzes, branching scenarios, and multimedia content can help maintain student interest and cater to different learning preferences and styles. One successful example in my classroom has been the inclusion of alternative project-based assessments. These projects are an engaging way for the students to demonstrate what they’ve learned by applying their knowledge to solve real-world problems or explore different phenomena.
Additionally, assessment strategies in online and blended learning should focus on formative feedback and competency-based evaluations. Providing opportunities for self-assessment and reflection can empower students to take ownership of their learning journey and apply their knowledge in meaningful ways. In my course, self-paced review modules allow students to revisit challenging topics and track their progress through mastery checks.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Online and Blended Mathematics Learning
The future of online and blended learning is promising, with advancements in artificial intelligence, adaptive learning technologies, and immersive experiences such as virtual and augmented reality. These innovations have the potential to further personalize learning experiences, providing real-time data and insights to support student success. Currently, I’m particularly fond of Minecraft Education Edition for its capability of presenting coding fundamentals in an immersive virtual environment.
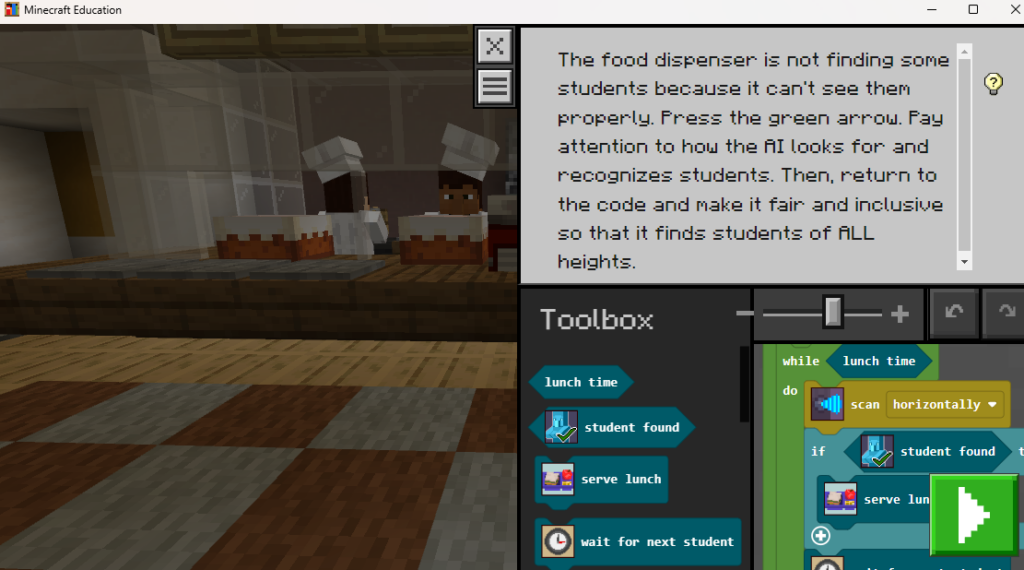
As educators, we must remain adaptable and open to exploring new pedagogical approaches and technologies. Continuously refining our learning strategies to uphold accessibility, inclusivity, and engagement will empower students to thrive in an increasingly digital world. Staying informed on emerging trends and leveraging innovative tools, helps us create transformative learning experiences that prepare students for academic success.
References:
Canvas. Instructure. (n.d.). https://www.instructure.com/canvas
CAST, Inc. (n.d.). The UDL guidelines. The UDL Guidelines. https://udlguidelines.cast.org/
Conceição, S. C. O., & Howles, L. (2020). Designing the online learning experience: Evidence-based principles and strategies. Taylor & Francis Group. Retrieved from Retrieved from ProQuest Ebook Central.
Minecraft Education Edition – Homepage. education.minecraft.net. (n.d.). https://education.minecraft.net/en-us
Rottmann, A., Barreto, D., & Rabidoux, S. (2020). What in the world is a learning management system? In Learning management systems: Choosing the right path for your organization. Retrieved from edtechbooks.org.